Antibody, Antibody Sampler Kit
Protein Folding and Stability Antibody Sampler Kit
- Catalog Number : AK0253
- Number : AK0253
-
Size:
Qty : - Price : Request 詢價
- Stock : Request
Introduction
The small regulatory protein ubiquitin is often covalently linked to many cellular proteins, labeling these targeted proteins for proteasome-mediated degradation. Ubiquitin is first activated by forming a thiolester complex with the E1 activation component. Activated ubiquitin is subsequently transferred to the ubiquitin-carrier protein E2, and then to an E3 ubiquitin ligase for final delivery to the ε-NH2 of the target protein lysine residue. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway has been implicated in a wide range of both normal biological processes and diseases. The ubiquitin-like protein family contains three small ubiquitin-related modifier proteins (SUMO-1, -2 and -3), neural precursor cell-expressed developmentally down-regulated protein 8 (NEDD8) and interferon-stimulated 15 kDa protein (ISG15). Their covalent attachment to target proteins is a reversible, multi-step process that is analogous to protein ubiquitination. Mature molecules are linked to the activating enzyme E1, conjugated to E2 and ligated to the target proteins by E3. Ubiquitin is the predominant regulator for the degradation of a wide range of target proteins while SUMO, NEDD8 and ISG15 modify a limited set of substrates to regulate various other biological processes. During ubiquitination, the combinatorial interaction of different E2 and E3 proteins produces variable substrate specificity. UBC3 and UBC3B are E2 ubiquitin-carrier proteins. The SCF (Skp1/CUL1/F-box) E3 ubiquitin ligase protein complex is composed of three protein components, including the S phase kinase associated protein 1 (Skp1), Cullin homolog 1 (CUL1) and the Skp2 F-box protein.
General Information
| Application | WB |
|---|---|
| Storage instruction | Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| Research topic | Protein folding and stability |



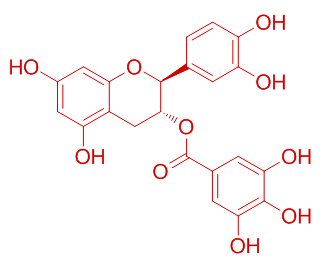
![1-Chloropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine](/img/nophoto.jpg)

.png)