Introduction
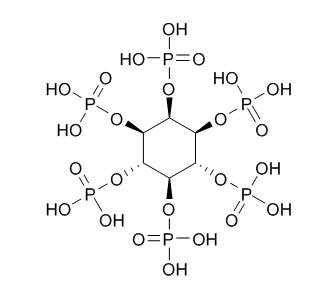
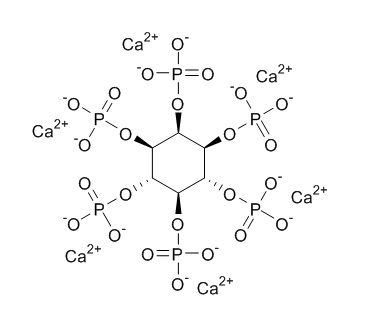
Phytic acid is the principal storage form of phosphorus in many plant tissues, especially bran and seeds. It can act as a cofactor in DNA repair by nonhomologous end-joining. It is a trypsin inhibitor, has chelating, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects, it forms an iron chelate which greatly accelerates Fe2+-mediated oxygen reduction yet blocks iron-driven hydroxyl radical generation and suppresses lipid peroxidation. High concentrations of phytic acid prevent browning and putrefaction of various fruits and vegetables by inhibiting polyphenol oxidase, it may be a substitute for presently employed preservatives.
General Information
| Application | Chemical |
|---|---|
| Cas No. | 83-86-3 |
| Purity | ≥98% |
| Molecular Weight | 660.04 |
| Formula | C6H18O24P6 |
| Solubility | DMSO, Pyridine, Methanol, Ethanol |
| Storage instruction | Store at 2-8℃ |
| Alias | Phytate;myo-Inositol hexakis(dihydrogen phosphate);myo-Inositol hexakis(phosphate);myo-Inositol hexaphosphate |





.png)